The triple constraint refer to the making and assessment time, cost and scope of project changes. Project management is essentially the art of making and assessing the time, cost and scope of project changes, so hence why the triple constraint is so important to project management. However each one of these factors needs to be equally balanced in order for project management to run effectively and efficiently, because if one of these factors changes or move then the others follow.
Figure 1: This is a diagram of triple constraint.
Describe the two primary diagrams most frequently used in project planning.
In a project plan each job is written down, resources are allocated and it works o3ut what tasks can be done at the same time.
The two primary diagrams most frequently used in project planning are PERT charts and Gantt charts.
PERT (Program Evaluation and Review Technique) charts: "are a graphical network model that depicts a project's tasks and the relationships between those tasks." The red lines/boxes denote the critical path.
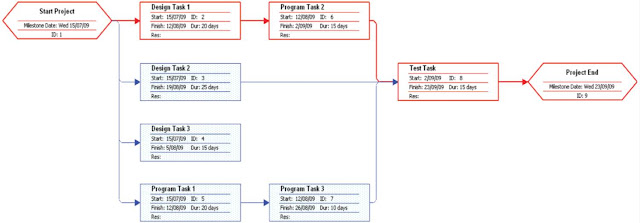 Figure 2: An example of a PERT chart.
Figure 2: An example of a PERT chart.
Identify the three primary areas a project manager must focus on managing to ensure success.
The two primary diagrams most frequently used in project planning are PERT charts and Gantt charts.
PERT (Program Evaluation and Review Technique) charts: "are a graphical network model that depicts a project's tasks and the relationships between those tasks." The red lines/boxes denote the critical path.
 Figure 2: An example of a PERT chart.
Figure 2: An example of a PERT chart.Gantt chart: "Is a simple bar chart that depicts project tasks against a calendar. Tasks are listed vertically and the projects time frame is listed horizontally."
Figure 3: An example of a Gantt chart.
Identify the three primary areas a project manager must focus on managing to ensure success.
To ensure success a project manager must focus on the following three primary areas:
-Managing people
-Managing communications
- Managing change
Outline 2 reasons why projects fail and two reasons why projects succeed.
-Managing people
-Managing communications
- Managing change
Outline 2 reasons why projects fail and two reasons why projects succeed.
References:
Baltzan, Phillips, Lynch, Blakey, Business Driven Information Systems, 1st Australian/New Zealand Edition, Mc Graw Hill, 2010.
TOMTSONGAS, 2011, Program Success Project & Program Management Success Factors, Scope, Time and Cost – Managing the Triple Constraint, http://programsuccess.wordpress.com/2011/05/02/scope-time-and-cost-managing-the-triple-constraint/, Visited 6/6/2011
Baltzan, Phillips, Lynch, Blakey, Business Driven Information Systems, 1st Australian/New Zealand Edition, Mc Graw Hill, 2010.
TOMTSONGAS, 2011, Program Success Project & Program Management Success Factors, Scope, Time and Cost – Managing the Triple Constraint, http://programsuccess.wordpress.com/2011/05/02/scope-time-and-cost-managing-the-triple-constraint/, Visited 6/6/2011


